 设计模式
设计模式
# 多线程—设计模式
# 两阶段终止—Two Phase Termination
# 用处
在一个线程 T1 中如何“优雅”终止线程 T2?这里的【优雅】指的是给 T2 一个料理后事的机会。
# 错误思路
使用线程对象的 stop() 方法停止线程
stop 方法会真正杀死线程,如果这时线程锁住了共享资源,那么当它被杀死后就再也没有机会释放锁,其它线程将永远无法获取锁
使用 System.exit(int) 方法停止线程
目的仅是停止一个线程,但这种做法会让整个程序都停止
# 两阶段终止模式
# interrupt 实现 🔥
@Slf4j(topic = "TwoPhaseTermination")
public class TwoPhaseTermination {
/* 监控线程 */
private Thread monitor;
/**
* 启动监控线程
*/
public void start(){
monitor = new Thread(()->{
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
while (true){
boolean flag = currentThread.isInterrupted();
if (flag){
log.debug("料理后事,优雅停机");
break;
}
try {
// 1 正常情况,被打断无需额外处理
log.debug("执行监控记录");
// 2 非正常情况,在 sleep、join、wait 中被中断
// 每1秒执行一次,释放CPU,所以sleep
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 由于 catch InterruptedException 后会清除中断标志,所以需要重设中断标志
currentThread.interrupt();
}
}
});
monitor.start();
}
/**
* 优雅停止监控线程
*/
public void stop(){
monitor.interrupt();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TwoPhaseTermination tpt = new TwoPhaseTermination();
tpt.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
tpt.stop();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
# volitile 实现 🔥
# 同步模式—保护(监控)性暂停—Guarded Suspension
# 定义
即 Guarded(监控) Suspension(暂停),用在一个线程等待另一个线程的执行结果
要点:
- 有一个结果需要从一个线程传递到另一个线程,让他们关联同一个 Guarded(监控) Object
- 如果有结果不断从一个线程到另一个线程那么可以使用消息队列(见生产者/消费者)
- JDK 中,join 的实现、Future 的实现,采用的就是此模式
- 因为要等待另一方的结果,因此归类到同步模式
对比 join 实现好处
- 下载线程执行完毕后还可以做其他事,因为已经有notifyAll通知了;而join则必须等待线程执行完毕!
# 实现—简单 🔥
@Slf4j(topic = "GuardedObject")
public class GuardedObject {
// 结果
private Object response;
/**
* 获取结果
*
* @return response
*/
public Object get() {
synchronized (this) {
while (response == null) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return response;
}
}
/**
* 产生结果
*
* @param response response
*/
public void complete(Object response) {
synchronized (this) {
// 给结果成员变量赋值,并唤醒等待线程
this.response = response;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1();
}
private static void test1(){
// // 模拟线程1等待线程2下载结果
GuardedObject guardedObject = new GuardedObject();
new Thread(() -> {
// 子线程下载
try {
List<String> download = Downloader.download();
log.debug("download complete...");
guardedObject.complete(download);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "download-thread").start();
log.debug("waiting...");
// 主线程阻塞等待
Object response = guardedObject.get();
log.debug("get response: [{}] lines", ((List<String>) response).size());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
下载工具类:
public class Downloader {
public static List<String> download() throws IOException {
URL url = new URL("https://www.qq.com/");
URLConnection conn = url.openConnection();
ArrayList<String> lines = new ArrayList<>();
try (
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
) {
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
lines.add(line);
}
}
return lines;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
执行结果:
17:03:36.977 [main] DEBUG GuardedObject - waiting...
17:03:37.473 [download-thread] DEBUG GuardedObject - download complete...
17:03:37.473 [main] DEBUG GuardedObject - get response: [1805] lines
2
3
# 实现—超时 🔥
@Slf4j(topic = "GuardedObject")
public class GuardedObject {
// 结果
private Object response;
/**
* 获取结果
*
* @param timeout 等待毫秒
* @return response
*/
public Object get(long timeout) {
synchronized (this) {
// 开始时间
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 经历时间
long passTime = 0;
while (response == null) {
// 这一轮循环实际还需要等待的时间
long waitTime = timeout - passTime;
// 经历时间超过了设置的等待最大时间,则退出循环。优化为还需等待的时间是否小于等于0
if (waitTime <= 0) {
break;
}
try {
// 这里只是等待timeout时间,等待完后又执行循环,需处理
// 并且若是虚假提前唤醒,则此时应该再等的时长应该少于timeout!!!用timeout减去已经cost的时长
this.wait(waitTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
passTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTime;// 计算经历时间
}
return response;
}
}
/**
* 产生结果
*
* @param response response
*/
public void complete(Object response) {
synchronized (this) {
// 给结果成员变量赋值,并唤醒等待线程
this.response = response;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test2();
}
private static void test2(){
// // 模拟线程1等待线程2下载结果
GuardedObject guardedObject = new GuardedObject();
new Thread(() -> {
// 子线程下载
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);// 模拟下载时间过长,超时了
List<String> download = Downloader.download();
log.debug("download complete...");
guardedObject.complete(download);// 这里如果传值为null,且不处理waitTime,则会多等一会
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "download-thread").start();
log.debug("waiting...");
// 主线程阻塞等待
Object response = guardedObject.get(2000);
log.debug("get response: {}", response);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
执行结果:
17:46:32.233 [main] DEBUG GuardedObject - waiting...
17:46:34.237 [main] DEBUG GuardedObject - get response: null
17:46:37.608 [download-thread] DEBUG GuardedObject - download complete...
2
3
# 实现—多任务版(实例不太恰当) 🔥
还是一对一关系,不是生产者消费者的多对多
图中 Futures 就好比居民楼一层的信箱(每个信箱有房间编号),左侧的 t0,t2,t4 就好比等待邮件的居民,右侧的 t1,t3,t5 就好比邮递员。
如果需要在多个类之间使用 GuardedObject 对象,作为参数传递不是很方便,因此设计一个用来解耦的中间类,这样不仅能够解耦【结果等待者】和【结果生产者】,还能够同时支持多个任务的管理。
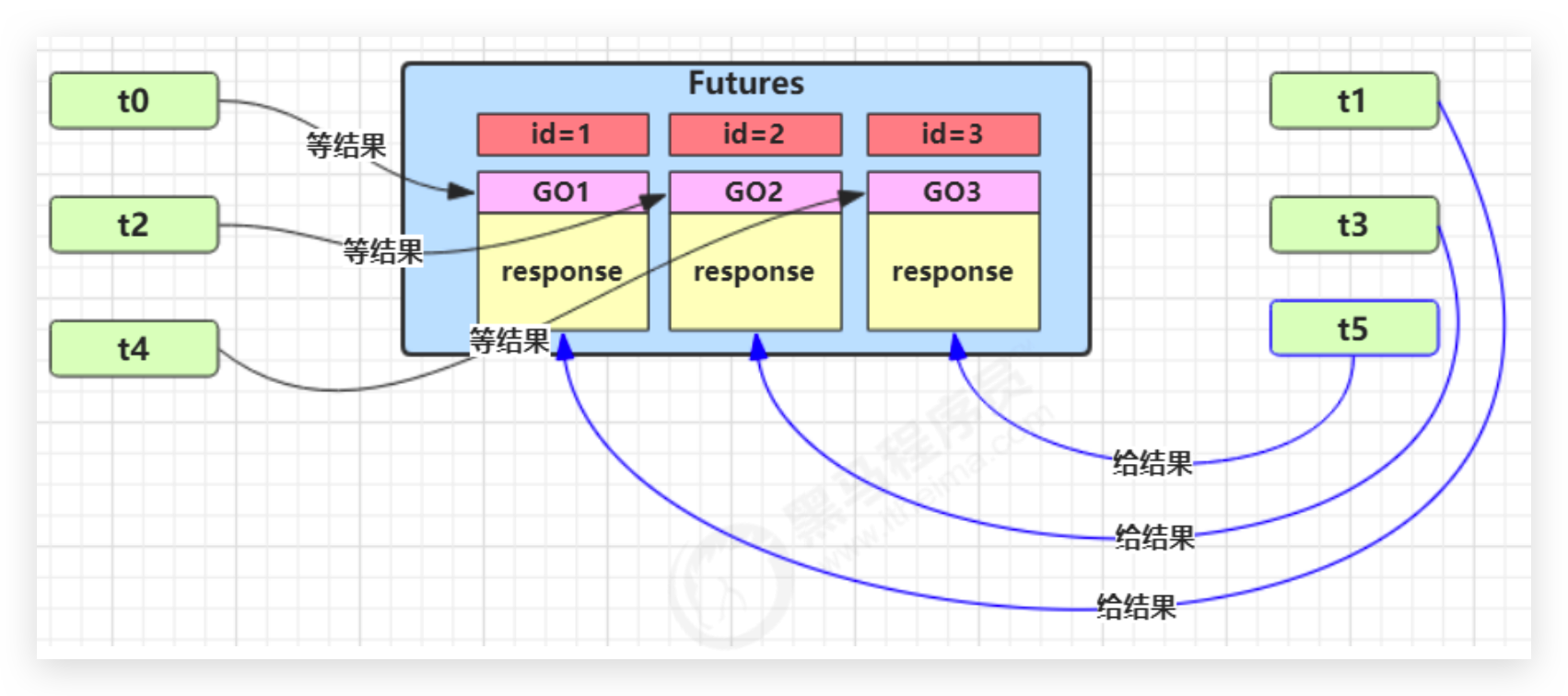
如下用邮箱的例子不是特别恰当,因为实际中不是一对一,应该邮递员少,并且用户实际是在不断等待信件的
@Slf4j(topic = "GuardedObject")
public class GuardedObject {
// 标识 guarded object
private int id;
// 结果
private Object response;
public GuardedObject() { }
public GuardedObject(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
/**
* 获取结果
*
* @return response
*/
public Object get() {
synchronized (this) {
while (response == null) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return response;
}
}
/**
* 获取结果
*
* @param timeout 等待毫秒
* @return response
*/
public Object get(long timeout) {
synchronized (this) {
// 开始时间
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 经历时间
long passTime = 0;
while (response == null) {
// 这一轮循环实际还需要等待的时间
long waitTime = timeout - passTime;
// 经历时间超过了设置的等待最大时间,则退出循环。优化为还需等待的时间是否小于等于0
if (waitTime <= 0) {
break;
}
try {
// 这里只是等待timeout时间,等待完后又执行循环,需处理
// 并且若是虚假提前唤醒,则此时应该再等的时长应该少于timeout!!!用timeout减去已经cost的时长
this.wait(waitTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
passTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTime;// 计算经历时间
}
return response;
}
}
/**
* 产生结果
*
* @param response response
*/
public void complete(Object response) {
synchronized (this) {
// 给结果成员变量赋值,并唤醒等待线程
this.response = response;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
public class Mailboxes {
// 初始化邮箱(多少户订阅,第一个订阅的id为1,类推)
public Mailboxes(int capacity) {
this.createGuardedObjects(capacity);
}
// 产生唯一id(在这里防止Person、Postman创建重复)
private static int i = 1;
private static synchronized int generateId(){
return i++;
}
// 对 GuardedObject 的创建、删除
private static Map<Integer, GuardedObject> boxes = new Hashtable<>();
/**
* 初始化总订阅
*/
private void createGuardedObjects(int capacity){
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < capacity; i1++) {
GuardedObject guardedObject = new GuardedObject(generateId());
boxes.put(guardedObject.getId(), guardedObject);
}
}
public static GuardedObject getGuardedObject(int id){
// 递送完就销毁,但是不能调用 remove,会有 ConcurrentModificationException
return boxes.get(id);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
@Slf4j(topic = "TestMailboxes")
public class TestMailboxes {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 邮局
// 5户人家需要订阅邮箱
final int CAPACITY = 5;
new Mailboxes(CAPACITY);
// 5户人家需要收信
for (int i = 1; i <= CAPACITY; i++) {
// 给用户分配id,并让他们等着收信就完事了
new Person(i).start();
}
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
// 生产信,派送(目前是邮递员和用户一一对应)
for (int i = 1; i <= CAPACITY; i++) {
new Postman(i, "内容" + i).start();
}
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "Person")
class Person extends Thread {
// 分配的 guardedObject id
private final int guardedObjectId;
public Person(int guardedObjectId) {
this.guardedObjectId = guardedObjectId;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 收信。收信人有门口邮箱号
log.debug("等待信件 id:{}", guardedObjectId);
GuardedObject guardedObject = Mailboxes.getGuardedObject(guardedObjectId);
// 不断等着收信就完事了
Object mail = guardedObject.get(5000);
log.debug("收到信 id:{}, 内容:{}", guardedObjectId, mail);
}
}
/**
* 邮局调用邮递员来派送邮件
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "Postman")
class Postman extends Thread {
// 信件上面都有目的地(这里用 guardedObject 的 id 表示)、信件内容
private int id;
private String mail;
public Postman(int id, String mail) {
this.id = id;
this.mail = mail;
}
@Override
public void run() {
GuardedObject guardedObject = Mailboxes.getGuardedObject(id);
log.debug("送信 id:{}, 内容:{}", id, mail);
guardedObject.complete(mail);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
结果如下:
23:14:37.927 [Thread-3] DEBUG Person - 等待信件 id:4
23:14:37.927 [Thread-0] DEBUG Person - 等待信件 id:1
23:14:37.927 [Thread-1] DEBUG Person - 等待信件 id:2
23:14:37.927 [Thread-4] DEBUG Person - 等待信件 id:5
23:14:37.927 [Thread-2] DEBUG Person - 等待信件 id:3
23:14:38.929 [Thread-6] DEBUG Postman - 送信 id:2, 内容:内容2
23:14:38.929 [Thread-5] DEBUG Postman - 送信 id:1, 内容:内容1
23:14:38.929 [Thread-7] DEBUG Postman - 送信 id:3, 内容:内容3
23:14:38.929 [Thread-0] DEBUG Person - 收到信 id:1, 内容:内容1
23:14:38.929 [Thread-1] DEBUG Person - 收到信 id:2, 内容:内容2
23:14:38.929 [Thread-2] DEBUG Person - 收到信 id:3, 内容:内容3
23:14:38.929 [Thread-8] DEBUG Postman - 送信 id:4, 内容:内容4
23:14:38.929 [Thread-9] DEBUG Postman - 送信 id:5, 内容:内容5
23:14:38.929 [Thread-3] DEBUG Person - 收到信 id:4, 内容:内容4
23:14:38.930 [Thread-4] DEBUG Person - 收到信 id:5, 内容:内容5
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 异步模式—生产者消费者 🔥
# 定义
与前面的保护性暂停中的 GuardObject 不同,不需要产生结果和消费结果的线程一一对应
消费队列可以用来平衡生产和消费的线程资源
生产者仅负责产生结果数据,不关心数据该如何处理,而消费者专心处理结果数据
消息队列是有容量限制的,满时不会再加入数据,空时不会再消耗数据
JDK 中各种阻塞队列,采用的就是这种模式
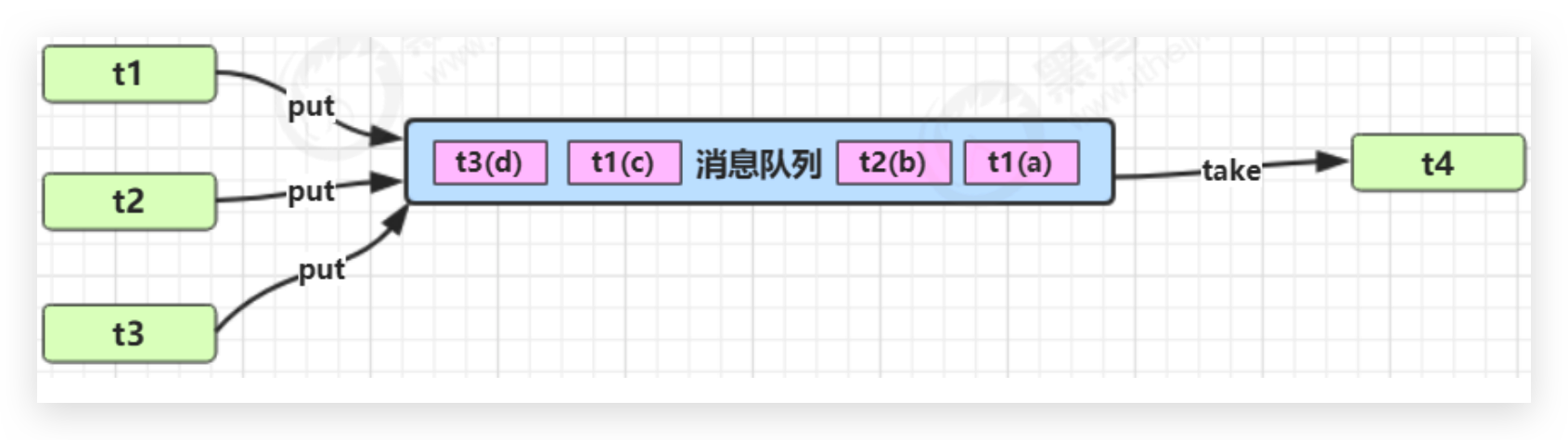
# 实现—消息队列—sync版 🔥
/**
* 消息队列,不同于MQ。本类是线程间的,MQ是进程间的
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "MessageQueue")
public class MessageQueue {
// 消息队列容器
private final LinkedList<Message> messages = new LinkedList<>();
// 消息队列容量
private int capacity;
public MessageQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
/**
* 生产存入消息
*/
public void put(Message message){
// 不断生产消息
while (true) {
synchronized (messages) {
// 检查队列是否满了
while (messages.size() == capacity) {
try {
log.debug("队列已满,生产者线程等待");
messages.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
messages.addLast(message);
log.debug("已生产消息, {},", message);
messages.notifyAll();// 有消息了,唤醒等待的消费线程
}
try {
// 生产完一个休息一下
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 消费消息
*
* @return
*/
public Message take() {
synchronized (messages) {
// 检查队列是否为空
while (messages.isEmpty()) {
try {
log.debug("队列为空,消费者线程等待");
messages.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Message message = messages.removeFirst();
log.debug("已消费消息, {},", message);
messages.notifyAll();// 已经被消费了,唤醒等待的生产者线程
return message;
}
}
}
class Message {
// 目前id没啥意义
private int id;
private Object value;
public Message(int id, Object value) {
this.id = id;
this.value = value;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Message{" +
"id=" + id +
", value=" + value +
'}';
}
}
class TestMessageQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MessageQueue messageQueue = new MessageQueue(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(() -> {
messageQueue.put(new Message(finalI, "值" + finalI));
}, "生产者" + i).start();
}
// 一天就5个人来消费
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
Message message = messageQueue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "消费者" + i).start();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
结果如下:
00:09:17.234 [生产者0] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已生产消息, Message{id=0, value=值0},
00:09:17.238 [生产者1] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已生产消息, Message{id=1, value=值1},
00:09:18.236 [消费者4] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已消费消息, Message{id=0, value=值0},
00:09:18.237 [消费者1] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已消费消息, Message{id=1, value=值1},
00:09:18.237 [消费者2] DEBUG MessageQueue - 队列为空,消费者线程等待
00:09:18.237 [消费者0] DEBUG MessageQueue - 队列为空,消费者线程等待
00:09:18.237 [消费者3] DEBUG MessageQueue - 队列为空,消费者线程等待
00:09:18.240 [生产者0] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已生产消息, Message{id=0, value=值0},
00:09:18.240 [消费者3] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已消费消息, Message{id=0, value=值0},
00:09:18.240 [消费者0] DEBUG MessageQueue - 队列为空,消费者线程等待
00:09:18.240 [消费者2] DEBUG MessageQueue - 队列为空,消费者线程等待
00:09:18.241 [生产者1] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已生产消息, Message{id=1, value=值1},
00:09:18.241 [消费者2] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已消费消息, Message{id=1, value=值1},
00:09:18.241 [消费者0] DEBUG MessageQueue - 队列为空,消费者线程等待
00:09:19.245 [生产者0] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已生产消息, Message{id=0, value=值0},
00:09:19.245 [消费者0] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已消费消息, Message{id=0, value=值0},
00:09:19.245 [生产者1] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已生产消息, Message{id=1, value=值1},
00:09:20.246 [生产者1] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已生产消息, Message{id=1, value=值1},
00:09:20.247 [生产者0] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已生产消息, Message{id=0, value=值0},
00:09:21.247 [生产者1] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已生产消息, Message{id=1, value=值1},
00:09:21.247 [生产者0] DEBUG MessageQueue - 已生产消息, Message{id=0, value=值0},
00:09:22.247 [生产者1] DEBUG MessageQueue - 队列已满,生产者线程等待
00:09:22.247 [生产者0] DEBUG MessageQueue - 队列已满,生产者线程等待
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 实现—生产消费 🔥
生产者(Productor)将产品交给店员(Clerk),而消费者(Consumer)从店员处取走产品,店员一次只能持有固定数量的产品(比如20),如果生产者试图生产更多的产品,店员会叫生产者停一下,如果店中有空位放产品了再通知生产者继续生产;如果店中没有产品了,店员会告诉消费者等一下,如果店中有产品了再通知消费者来取走产品。
分析:
是否是多线程问题?是,生产者线程,消费者线程
是否有共享数据?是,店员(或产品)
是否涉及线程的通信?是
# sync 版
class Productor implements Runnable {
private final Product product;
public Productor(Product product) {
this.product = product;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (product) {
// while 和 wait 一起使用;不能单独使用 if,可能会缺少一次判断
// 不能使用 if...else,会导致 wait 唤醒后即使满足条件也不能生产或消费,浪费了 OS 资源
while (product.productNum >= 20) {
try {
product.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
product.productNum++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":生产第" + product.productNum + "个产品");
product.notifyAll();
}
try {
// 放在同步外更合理,其他线程可以此时抢占资源
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable {
private final Product product;
public Consumer(Product product) {
this.product = product;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (product) {
// while 和 wait 一起使用;不能单独使用 if,可能会缺少一次判断
// 不能使用 if...else,会导致 wait 唤醒后即使满足条件也不能生产或消费,浪费了 OS 资源
while (product.productNum <= 0) {
try {
product.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":消费第" + product.productNum + "个产品");
product.productNum--;
product.notifyAll();
}
// 放在同步外更合理,其他线程可以此时抢占资源
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class Product {
// 产品数量
int productNum = 0;
}
public class PCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Product product = new Product();
new Thread(new Productor(product), "生产者1").start();
new Thread(new Productor(product), "生产者2").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(product), "消费者1").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(product), "消费者2").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(product), "消费者3").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(product), "消费者4").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(product), "消费者5").start();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
# Lock 版本
class Productor implements Runnable {
private final Product product;
public Productor(Product product) {
this.product = product;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
product.lock.lock();
// while 和 wait 一起使用;不能单独使用 if,可能会缺少一次判断
// 不能使用 if...else,会导致 wait 唤醒后即使满足条件也不能生产或消费,浪费了 OS 资源
while (product.productNum >= 20) {
try {
product.productor.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
product.productNum++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":生产第" + product.productNum + "个产品");
product.consumer.signalAll();
} finally {
product.lock.unlock();
}
try {
// 放在同步外更合理,其他线程可以此时抢占资源
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable {
private final Product product;
public Consumer(Product product) {
this.product = product;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
product.lock.lock();
// while 和 wait 一起使用;不能单独使用 if,可能会缺少一次判断
// 不能使用 if...else,会导致 wait 唤醒后即使满足条件也不能生产或消费,浪费了 OS 资源
while (product.productNum <= 0) {
try {
product.consumer.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":消费第" + product.productNum + "个产品");
product.productNum--;
product.productor.signalAll();
} finally {
product.lock.unlock();
}
// 放在同步外更合理,其他线程可以此时抢占资源
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class Product {
// 产品数量
int productNum = 0;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition productor = lock.newCondition();
Condition consumer = lock.newCondition();
}
public class PCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Product product = new Product();
new Thread(new Productor(product), "生产者1").start();
new Thread(new Productor(product), "生产者2").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(product), "消费者1").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(product), "消费者2").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(product), "消费者3").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(product), "消费者4").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(product), "消费者5").start();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
