 JPA示例(旧)
JPA示例(旧)
# CRUD 案例
# 常用注解 🔥
# @Entity 🔥
作用:指定当前类是实体类。
# @Table 🔥
作用:指定实体类和表之间的对应关系。
属性:
name:指定数据库表的名称,不指定则为类名首字母小写,若是多个单词则默认变为下划线连接
# @Id 🔥
作用:指定当前字段是主键。
# @GeneratedValue 🔥
作用:指定主键的生成策略。
属性:
strategy:指定主键生成策略。JPA 提供的四种标准用法为TABLE,SEQUENCE,IDENTITY,AUTO。IDENTITY:主键由数据库自动生成(主要是自动增长型,必须数据库底层支持,如 MySQL)@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long custId;1
2
3SEQUENCE:根据底层数据库的序列来生成主键,条件是数据库支持序列,如 Oracle。@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE,generator="payablemoney_seq") @SequenceGenerator(name="payablemoney_seq", sequenceName="seq_payment") private Long custId;1
2
3
4//@SequenceGenerator源码中的定义 @Target({TYPE, METHOD, FIELD}) @Retention(RUNTIME) public @interface SequenceGenerator { //表示该表主键生成策略的名称,它被引用在@GeneratedValue中设置的“generator”值中 String name(); //属性表示生成策略用到的数据库序列名称。 String sequenceName() default ""; //表示主键初识值,默认为0 int initialValue() default 0; //表示每次主键值增加的大小,例如设置1,则表示每次插入新记录后自动加1,默认为50 int allocationSize() default 50; }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13AUTO:主键由程序控制(测试了下使用的是 TABLE)@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) private Long custId;1
2
3TABLE:使用一个特定的数据库表格来保存主键@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.TABLE, generator="payablemoney_gen") @TableGenerator(name = "pk_gen", table="tb_generator", pkColumnName="gen_name", valueColumnName="gen_value", pkColumnValue="PAYABLEMOENY_PK", allocationSize=1 ) private Long custId;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10//@TableGenerator的定义: @Target({TYPE, METHOD, FIELD}) @Retention(RUNTIME) public @interface TableGenerator { //表示该表主键生成策略的名称,它被引用在@GeneratedValue中设置的“generator”值中 String name(); //表示表生成策略所持久化的表名,例如,这里表使用的是数据库中的“tb_generator”。 String table() default ""; //catalog和schema具体指定表所在的目录名或是数据库名 String catalog() default ""; String schema() default ""; //属性的值表示在持久化表中,该主键生成策略所对应键值的名称。例如在“tb_generator”中将“gen_name”作为主键的键值 String pkColumnName() default ""; //属性的值表示在持久化表中,该主键当前所生成的值,它的值将会随着每次创建累加。例如,在“tb_generator”中将“gen_value”作为主键的值 String valueColumnName() default ""; //属性的值表示在持久化表中,该生成策略所对应的主键。例如在“tb_generator”表中,将“gen_name”的值为“CUSTOMER_PK”。 String pkColumnValue() default ""; //表示主键初识值,默认为0。 int initialValue() default 0; //表示每次主键值增加的大小,例如设置成1,则表示每次创建新记录后自动加1,默认为50。 int allocationSize() default 50; UniqueConstraint[] uniqueConstraints() default {}; } /*==================================================================*/ //这里应用表tb_generator,定义为 : CREATE TABLE tb_generator ( id NUMBER NOT NULL, gen_name VARCHAR2(255) NOT NULL, gen_value NUMBER NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(id) )1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# @Column 🔥
作用:指定实体类属性和数据库表之间的对应关系
属性:
name:指定数据库表的列名称。不指定则为属性名,若是多个单词则默认变为下划线连接length:长度unique:是否唯一nullable:是否可以为空inserttable:是否可以插入updateable:是否可以更新columnDefinition: 定义建表时创建此列的 DDLsecondaryTable: 从表名。如果此列不建在主表上(默认建在主表),该属性定义该列所在从表的名字搭建开发环境[重点]
# @Transient 🔥
瞬态,即不会被映射到数据库表字段
# @OneToMany
建立一对多的关系映射
属性:
mappedBy:🔥指定在从表实体类中引用主表对象的名称,一般用于主表放弃外键维护或被维护表放弃维护中间表fetch:指定是否采用延迟加载,枚举类FetchTypeLAZY(默认),EAGER
cascade:指定要使用的级联操作,枚举类CascadeTypeALL,PERSIST,MERGE,REMOVE,REFRESH,DETACH;
orphanRemoval:是否使用孤儿删除,true;false(默认)targetEntity:指定多的多方的类的字节码,可省略会自动推倒
# @ManyToOne
建立多对一的关系
属性:
fetch:指定是否采用延迟加载(同上)cascade:指定要使用的级联操作(同上)optional:关联是否可选。如果设置为 false,则必须始终存在非空关系。默认为 truetargetEntity:指定一的一方实体类字节码,可省略会自动推导
# @ManyToMany
用于映射多对多关系
属性:
fetch:指定是否采用延迟加载(同上)cascade:指定要使用的级联操作(同上)targetEntity:配置目标的实体类。映射多对多的时候不用写。可省略会自动推导
# @OneToOne
# @JoinColumn 🔥
用于定义主键字段和外键字段的对应关系,主要用于从表中定义外键的引用
属性:
name:指定外键字段的名称,不配置则根据被维护表中属性名和referencedColumnName组合referencedColumnName:指定引用主表的主键字段名称unique:是否唯一。默认 falsenullable:是否允许为空。默认 true。insertable:是否允许插入。默认 true。updatable:是否允许更新。默认 true。columnDefinition:列的定义信息。
# @JoinTable
针对中间表的配置,主要用于维护表来设置
属性:
name:配置中间表的名称,不配置则自动根据维护表和被维护表的类名组合来生成@joinColumns:需要中间表的外键字段关联当前实体类所对应表的主键字段@inverseJoinColumn:需要中间表的外键字段关联对方表的主键字段
# 配置
# Maven 坐标导入
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 配置文件
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql:///sleeve?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
username: root
password: w111111
jpa:
hibernate:
# 一般只推荐 update(但是修改字段也不会重新生成表); create 会清空之前的表; create-drop 一般用在测试, 会话完成后清空表。
# 其实也不推荐使用, 后续会置为 none
ddl-auto: create-drop
show-sql: true # 显示
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 建立 ORM 🔥
创建客户的数据库表(不创建也行)
在实体类上使用 JPA 注解的形式配置映射关系
所有的注解都是使用 JPA 的规范提供的注解,导入
javax.persistence下注解包@Entity @Table(name = "cst_customer") public class Customer { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) @Column(name = "cust_id") private Long custId; //客户的主键 @Column(name = "cust_name") private String custName;//客户名称 @Column(name = "cust_source") private String custSource;//客户来源 @Column(name = "cust_level") private String custLevel;//客户级别 @Column(name = "cust_industry") private String custIndustry;//客户所属行业 @Column(name = "cust_phone") private String custPhone;//客户的联系方式 @Column(name = "cust_address") private String custAddress;//客户地址 //getter setter }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# Repository 接口
别忘了接口之间是可以多继承的!!!
/**
* JpaRepository<实体类类型,主键类型>:用来完成基本CRUD操作
* JpaSpecificationExecutor<实体类类型>:用于复杂查询(分页等查询操作)
*/
public interface CustomerDao extends JpaRepository<Customer,Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Customer> {
}
2
3
4
5
6
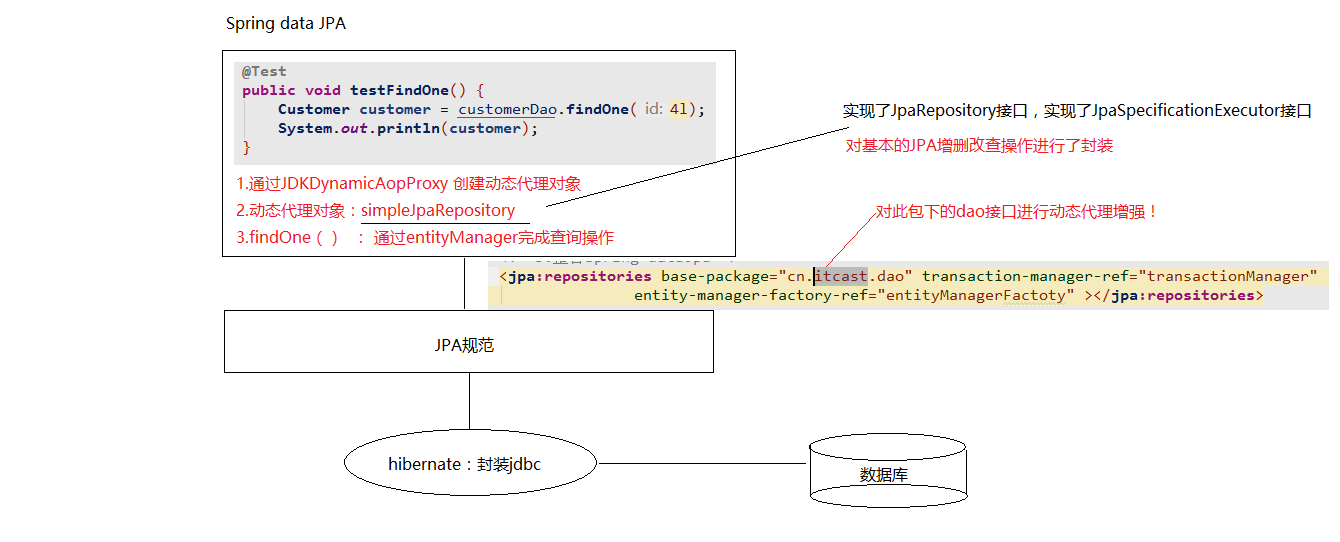
# 基本CRUD和复杂查询
# 接口中的定义好的方法
以下是继承了JpaRepository接口后获得的
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")//locations可省略
public class CustomerDaoTest {
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
@Test
public void testFindById() {
Optional<Customer> optional = customerDao.findById(3L);
System.out.println(optional.orElse(null));
}
/**
* 根据ID查询(立即加载,底层调用find()方法)
*/
@Test
public void testFindOne() {
Customer customer = customerDao.findOne(3L);
System.out.println(customer);
}
/**
* 根据ID查询(延迟加载,底层调用getReference()方法)
* 返回的是动态代理对象;什么时候用,什么时候查询(IDEA需要去掉Debug中几个选项才可以看到)
*/
@Test
@Transactional
public void testGetOne() {
Customer customer = customerDao.getOne(3L);
System.out.println(customer);
}
/**
* 查询所有
*/
@Test
public void testFindAll() {
List<Customer> customerList = customerDao.findAll();
System.out.println(customerList);
}
/**
* 保存或更新(!!!不要直接使用这个来更新,否则会将其他没有值的数据置null。)
* 根据传递的对象是否包含主键ID,不包含则是保存;包含则是先根据ID查询数据,并更新
*
* 更新需要根据ID手动查找,然后修改再保存!!!
*/
@Test
public void testSave() {
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setCustName("黑马程序员");
customer.setCustAddress("西安");
customerDao.save(customer);
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setCustId(8L);
customer.setCustName("黑马程序员牛逼");
customer.setCustAddress("西安");
customer.setCustLevel("VIP");
customerDao.save(customer);
}
/**
* 根据ID删除(底层是先查询,若有再删除)
*/
@Test
public void testDelete() {
customerDao.delete(8L);
}
/**
* 统计查询
*/
@Test
public void testCount() {
long count = customerDao.count();
System.out.println(count);
}
/**
* 根据ID判断是否存在该数据(可以根据查询的对象是否为null;或统计出的数量是否大于0(这里底层用的是这个))
*/
@Test
public void testExists() {
boolean exists = customerDao.exists(7L);
System.out.println(exists);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
# 方法名称规则查询
方法命名规则查询就是根据方法的名字,就能创建查询,是对JPQL更深层次封装。只需要按照Spring Data JPA提供的方法命名规则定义方法的名称,不需要配置JPQL语句就可以完成查询工作。Spring Data JPA在程序执行的时候会根据方法名称进行解析,并自动生成查询语句进行查询。
按照Spring Data JPA 定义的规则,查询方法以**findBy开头,涉及条件查询时,条件的属性用条件关键字连接,要注意的是:条件属性首字母需大写**。框架在进行方法名解析时,会先把方法名多余的前缀截取掉,然后对剩下部分进行解析。也可以删除。
会根据先后顺序传参!!名称无所谓
public interface CustomerDao extends JpaRepository<Customer,Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Customer> {
/**
* 方法名称查询(精准匹配)
*/
Customer findByCustName(String custName);
/**
* 方法名称查询(like模糊匹配)
*/
List<Customer> findByCustNameLike(String custName);
/**
* 方法名称查询(使用客户名称模糊匹配和客户行业精准匹配)
*/
List<Customer> findByCustNameLikeAndCustIndustry(String custName,String custIndustry);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")//locations可省略
public class JPQLTest {
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
/**
* 测试方法命名查询
*/
@Test
public void testFindByCustName(){
Customer customer = customerDao.findByCustName("传智播客6");
System.out.println(customer);
}
/**
* 测试方法命名查询(模糊匹配)
*/
@Test
public void testFindByCustNameLike(){
List<Customer> customerList = customerDao.findByCustNameLike("传智%");
System.out.println(customerList);
}
/**
* 测试方法命名查询(使用客户名称模糊匹配和客户行业精准匹配)
*/
@Test
public void testFindByCustNameLikeAndCustIndustry(){
List<Customer> customerList = customerDao.findByCustNameLikeAndCustIndustry("传智%","IT");
System.out.println(customerList);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
具体的关键字,使用方法和生产成SQL如下表所示
| Keyword | Sample | JPQL |
|---|---|---|
| And | findByLastnameAndFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
| Or | findByLastnameOrFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 |
| Is,Equals | findByFirstnameIs, findByFirstnameEquals | … where x.firstname = ?1 |
| Between | findByStartDateBetween | … where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 |
| LessThan | findByAgeLessThan | … where x.age < ?1 |
| LessThanEqual | findByAgeLessThanEqual | … where x.age ⇐ ?1 |
| GreaterThan | findByAgeGreaterThan | … where x.age > ?1 |
| GreaterThanEqual | findByAgeGreaterThanEqual | … where x.age >= ?1 |
| After | findByStartDateAfter | … where x.startDate > ?1 |
| Before | findByStartDateBefore | … where x.startDate < ?1 |
| IsNull | findByAgeIsNull | … where x.age is null |
| IsNotNull,NotNull | findByAge(Is)NotNull | … where x.age not null |
| Like | findByFirstnameLike | … where x.firstname like ?1 |
| NotLike | findByFirstnameNotLike | … where x.firstname not like ?1 |
| StartingWith | findByFirstnameStartingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %) |
| EndingWith | findByFirstnameEndingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %) |
| Containing | findByFirstnameContaining | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %) |
| OrderBy | findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc | … where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc |
| Not | findByLastnameNot | … where x.lastname <> ?1 |
| In | findByAgeIn(Collection ages) | … where x.age in ?1 |
| NotIn | findByAgeNotIn(Collection age) | … where x.age not in ?1 |
| TRUE | findByActiveTrue() | … where x.active = true |
| FALSE | findByActiveFalse() | … where x.active = false |
| IgnoreCase | findByFirstnameIgnoreCase | … where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |
# JPQL 查询
- 特有的查询:需要在Dao接口上配置方法
- 在新添加的方法上,使用**
@Query注解的形式配置JPQL查询语句**
public interface CustomerDao extends JpaRepository<Customer,Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Customer> {
/**
* 根据客户名称查询客户。使用JPQL查询
* ?1代表参数的占位符,其中1对应方法中的参数索引
*/
@Query("from Customer where custName = ?1")
Customer findByName(String custName);
/**
* 根据客户名称和客户ID查询客户。使用JPQL查询
* ?1代表参数的占位符,其中1对应方法中的参数索引。不指定则按照方法中参数位置对应
*/
@Query("from Customer where custName = ?1 and custId=?2")
Customer findByNameAndId(String custName,Long custId);
/**
* 根据ID更新客户名称。使用JPQL
* ?1代表参数的占位符,其中1对应方法中的参数索引。不指定则按照方法中参数位置对应。“:参数名称“ 也可以当做占位符
*/
@Query("update Customer set custName = ?1 where custId = ?2")
@Modifying//代表是更新操作
void updateNameById(String custName,Long custId);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")//locations可省略
public class JPQLTest {
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
@Test
public void testFindByName() {
Customer customer = customerDao.findByName("传智播客6");
System.out.println(customer);
}
@Test
public void testFindByNameAndId() {
Customer customer = customerDao.findByNameAndId("传智播客", 5L);
System.out.println(customer);
}
/**
* Spring Data JPA中使用JPQL完成 更新、删除操作需要手动添加事务,但默认执行后会回滚事务,需要添加注解设置为不回滚
*/
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(value = false)
public void testUpdateNameById() {
customerDao.updateNameById("传智播客最牛逼", 5L);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# SQL 语句查询
- 特有的查询:需要在Dao接口上配置方法
- 在新添加的方法上,使用**
@Query注解的形式配置SQL查询语句**,还需设置nativeQuery属性
public interface CustomerDao extends JpaRepository<Customer,Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Customer> {
/**
* 使用SQL查询全部客户/模糊查询
* nativeQuery:默认false为JPQL查询,true为SQL查询
*/
//@Query(value = "select * from cst_customer", nativeQuery = true)
@Query(value = "select * from cst_customer where cust_name like ?1", nativeQuery = true)
List<Object[]> findBySQL(String name);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")//locations可省略
public class JPQLTest {
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
@Test
public void testFindBySQL() {
List<Object[]> list = customerDao.findBySQL("传智播客%");
for (Object[] obj : list) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(obj));
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Specification 动态查询
以下是继承了JpaSpecificationExecutor接口后获得的
Spring Data JPA中可以通过JpaSpecificationExecutor接口查询。相比JPQL,其优势是类型安全,更加的面向对象。
T findOne(Specification<T> spec);//查询单个对象List<T> findAll(Specification<T> spec);//查询列表Page<T> findAll(Specification<T> spec, Pageable pageable);- Pageable:分页参数
- 返回值:Spring Data JPA提供的分页Bean
List<T> findAll(Specification<T> spec, Sort sort);//排序查询long count(Specification<T> spec);//统计查询
对于JpaSpecificationExecutor,这个接口基本是围绕着Specification接口来定义的。我们可以简单的理解为,Specification构造的就是查询条件。
/**
* root :Root接口,代表查询的根对象,可以通过root获取实体中的属性
* query :代表一个顶层查询对象,用来自定义查询(用的少,但是很强大)
* cb :用来构建查询,此对象里有很多条件方法
**/
public Predicate toPredicate(Root<T> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb);
2
3
4
5
6
7
/**
* 1.实现Specification接口(提供泛型:查询的对象类型)
* 2.实现toPredicate方法(构造查询条件)
* 3.需要借助方法参数中的两个参数(
* root:获取需要查询的对象属性(不是数据库中字段名!!)
* CriteriaBuilder:构造查询条件的,内部封装了很多的查询条件(模糊匹配,精准匹配)
**/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class SpecTest {
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
/**
* 单条件查询,根据客户名称查询单个客户对象(equal)
*/
@Test
public void testFindOne1() {
Specification<Customer> specification = new Specification<Customer>() {
public Predicate toPredicate(Root<Customer> root, CriteriaQuery<?> criteriaQuery, CriteriaBuilder criteriaBuilder) {
//1.获取比较的属性
Path<Object> custName = root.get("custName");
//2.构造查询条件
//第1个参数为比较的属性(Path对象);第2个参数为要比较的值
return criteriaBuilder.equal(custName, "博学谷");
}
};
Customer customer = customerDao.findOne(specification);
System.out.println(customer);
}
/**
* 多条件查询,根据客户名和客户所属行业查询单个客户(equal,and)
*/
@Test
public void testFindOne2() {
Specification<Customer> specification = (root, criteriaQuery, criteriaBuilder) -> {
Path<Object> custName = root.get("custName");
Path<Object> custIndustry = root.get("custIndustry");
Predicate predicate1 = criteriaBuilder.equal(custName, "传智播客");
Predicate predicate2 = criteriaBuilder.equal(custIndustry, "IT");
//组合谓词
return criteriaBuilder.and(predicate1, predicate2);//还有or等等方法来组合
};
Customer customer = customerDao.findOne(specification);
System.out.println(customer);
}
/**
* 普通查询;排序查询;分页查询,根据客户名模糊匹配查询客户列表(like);
* equal :直接的到path对象(属性),然后进行比较即可
* gt,lt,ge,le,like : 得到Path对象,根据Path指定比较的参数类型,再去进行比较
*/
@Test
public void testFindAll1() {
Specification<Customer> specification = ((root, criteriaQuery, criteriaBuilder) -> {
Path<Object> custName = root.get("custName");
return criteriaBuilder.like(custName.as(String.class), "%传智%");//或在获取Path时直接封装为String类型
});
//普通查询
List<Customer> customerList1 = customerDao.findAll(specification);
//排序查询
//第一个参数:排序的顺序(倒序,正序);第二个参数:排序的属性名称(不是字段名!)
Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "custId");
List<Customer> customerList2 = customerDao.findAll(specification, sort);
//分页查询
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(0,2);//页码(从0开始),每页显示条数
Page<Customer> customerPage = customerDao.findAll(specification, pageable);
System.out.println("总记录数:" + customerPage.getTotalElements());
System.out.println("总页数:" + customerPage.getTotalPages());
System.out.println("分页查询的数据:" + customerPage.getContent());
}
/**
* Specification的多表查询
*/
@Test
public void testFind() {
Specification<LinkMan> specification = (root, criteriaQuery, criteriaBuilder) -> {
//Join代表链接查询,通过root对象获取
//创建的过程中,第一个参数为关联对象的属性名称,第二个参数为连接查询的方式(inner,left,right)
//JoinType.LEFT : 左外连接,JoinType.INNER:内连接,JoinType.RIGHT:右外连接
Join<LinkMan, Customer> join = root.join("customer",JoinType.INNER);
return criteriaBuilder.like(join.get("custName").as(String.class),"传智播客1");
}
};
List<LinkMan> list = linkManDao.findAll(specification);
for (LinkMan linkMan : list) {
System.out.println(linkMan);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
方法对应关系
方法名称 Sql对应关系 equle filed = value gt(greaterThan ) filed > value lt(lessThan ) filed < value ge(greaterThanOrEqualTo ) filed >= value le( lessThanOrEqualTo) filed <= value notEqule filed != value like filed like value notLike filed not like value
# 多表操作
在实际开发中,我们数据库的表难免会有相互的关联关系,在操作表的时候就有可能会涉及到多张表的操作。而在这种实现了ORM思想的框架中(如JPA),可以让我们通过操作实体类就实现对数据库表的操作。所以今天我们的学习重点是:掌握配置实体之间的关联关系。
- 第一步:首先确定两张表之间的关系。(如果关系确定错了,后面做的所有操作就都不可能正确。)
- 第二步:在数据库中实现两张表的关系
- 第三步:在实体类中描述出两个实体的关系
- 第四步:配置出实体类和数据库表的关系映射(重点)
# 一对多
案例:客户和联系人的案例(一对多关系,一个客户可以具有多个联系人,一个联系人从属于一家公司)
- 客户:一家公司
- 联系人:这家公司的员工
分析步骤:
明确表关系:一对多关系
确定表关系(外键)
- 主表:客户表
- 从表:联系人表,在从表添加外键
编写实体类,再实体类中描述表关系(包含关系)
- 客户:再客户的实体类中包含一个联系人的集合
- 联系人:在联系人的实体类中包含一个客户的对象
配置映射关系
- 使用 JPA 注解配置一对多映射关系
@Entity
@Table(name = "cst_customer")
public class Customer {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "cust_id")
private Long custId; //客户的主键
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "customer")//主表放弃维护外键
private Set<LinkMan> linkMans = new HashSet<>();
@Column(name = "cust_name")
private String custName;//客户名称
...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@Entity
@Table(name = "cst_linkman")
public class LinkMan implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "lkm_id")
private Long lkmId;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "lkm_cust_id",referencedColumnName = "cust_id")
private Customer customer;
@Column(name = "lkm_name")
private String lkmName;
...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class One2ManyTest {
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
@Autowired
private LinkManDao linkManDao;
@Test
@Transactional//开启事务
@Rollback(false)//不回滚
public void testSave() {
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setCustName("腾讯");
LinkMan linkMan = new LinkMan();
linkMan.setLkmName("小马");
customer.getLinkMans().add(linkMan);
linkMan.setCustomer(customer);
customerDao.save(customer);
linkManDao.save(linkMan);
}
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)//设置为不回滚
public void testDelete() {
customerDao.delete(3L);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
删除操作的说明如下
删除从表数据:可以随时任意删除
删除主表数据:
没有从表数据引用:随便删
有从表数据:
- 在默认情况下,它会把外键字段置为null,然后删除主表数据。如果在数据库的表结构上,外键字段有非空约束,默认情况就会报错了
- 如果配置了放弃维护关联关系的权利,则不能删除(与外键字段是否允许为null,没有关系)因为在删除时,它根本不会去更新从表的外键字段了
- 如果还想删除,使用级联删除引用(在实际开发中,级联删除请慎用!(在一对多的情况下))
级联:操作一个对象的同时操作他的关联对象
- 级联操作:
1.需要区分操作主体
2.需要在操作主体的实体类上(主表或维护表),添加级联属性
cascade(需要添加到多表映射关系的注解上) - 级联添加,案例:当我保存一个客户的同时保存联系人(在代码中只需保存客户!)
- 级联删除,案例:当我删除一个客户的同时删除此客户的所有联系人,有中间表会先删除中间表(在代码中只需删除客户!)
# 多对多
案例:用户和角色(多对多关系)
分析步骤:
明确表关系:多对多关系
确定表关系(中间表)
编写实体类,再实体类中描述表关系(包含关系)
- 用户:包含角色的集合
- 角色:包含用户的集合
配置映射关系
- 使用 JPA 注解配置多对多映射关系
@Entity
@Table//不配置name则为类目首字母小写
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column//不配置字段名则为属性名
private Long userId;
@ManyToMany
//维护中间表
@JoinTable(
name = "sys_user_role",
//当前对象在中间表中的外键
joinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "sys_user_id",referencedColumnName = "userId")},
//对方对象在中间表中的外键
inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "sys_role_id",referencedColumnName = "roleId")}
)
private Set<Role> roles = new HashSet<>();
...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
@Entity
@Table
public class Role {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column
private Long roleId;
@ManyToMany(mappedBy = "roles")//被维护表放弃维护中间表!
private Set<User> users = new HashSet<>();
...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
其他删除/级联等同一对多,删除时会先删除中间表数据
# 对象导航查询
对象图导航检索方式是根据已经加载的对象,导航到他的关联对象。它利用类与类之间的关系来检索对象。例如:我们通过ID查询方式查出一个客户,可以调用Customer类中的getLinkMans()方法来获取该客户的所有联系人。对象导航查询的使用要求是:两个对象之间必须存在关联关系。
对象导航查询
- 从一方查询多方:默认延迟加载
- 从多方查询一方:默认立即加载
可以修改配置将其改为立即加载(不推荐!),fetch配置在多表关系中主体(或一方或多方)的注解上,查看3.3
# Specification 动态查询
如基本 CRUD 和复杂查询章节
